Fórmulas do Paralelepípedo — volume, áreas e diagonal
Consulte em um só lugar as fórmulas do paralelepípedo (retângulo e oblíquo), com exemplos resolvidos em formato vertical e exercícios com gabarito.
1) O que é paralelepípedo?
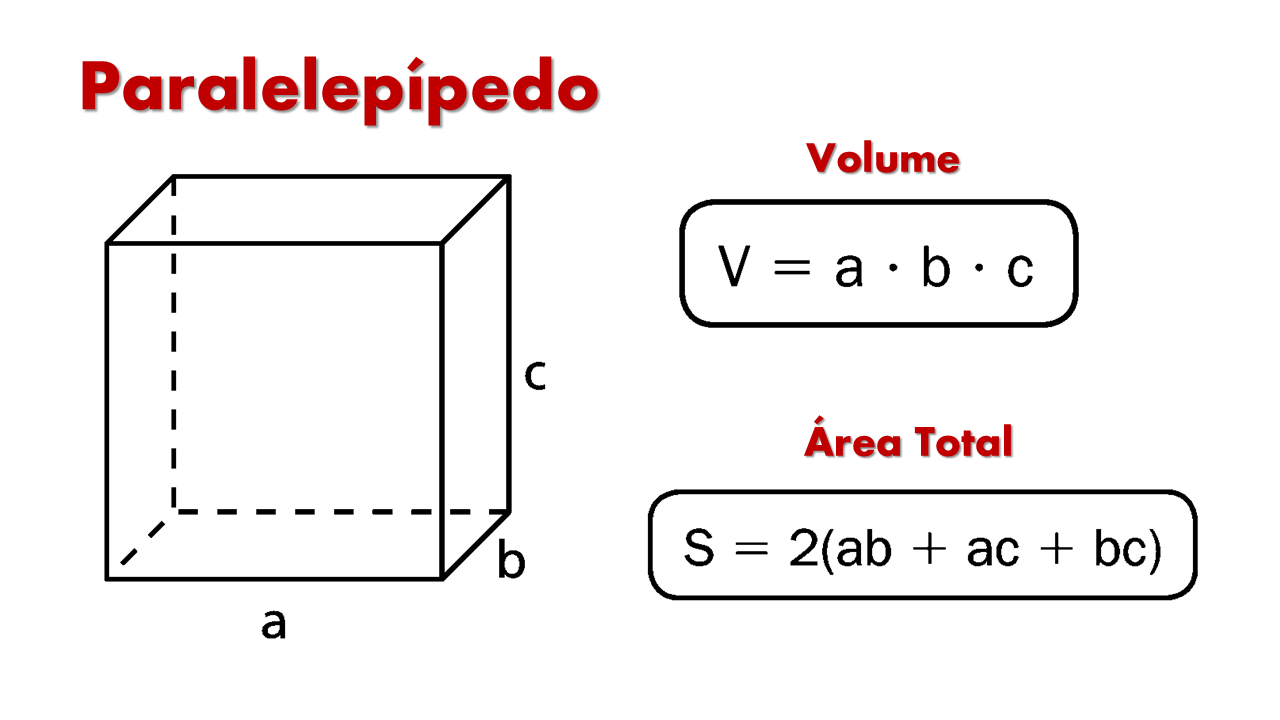
É um prisma cujas faces opostas são paralelogramos. No caso mais usado (paralelepípedo retângulo), as 6 faces são retângulos. Elementos: 6 faces, 12 arestas e 8 vértices. O cubo é um caso particular com \(a=b=c\).
2) Formulário essencial
Volume
Geral (reto e oblíquo): \(V = A_{\text{base}}\cdot h\) (altura perpendicular à base).
Retângulo (arestas ortogonais): \(V = a\cdot b\cdot c\).
Área total e área lateral (retângulo)
Área total: \(A_t = 2(ab+ac+bc)\).
Área lateral (tomando \(a\times b\) como base): \(A_l = 2c(a+b)\).
Se a base for \(b\times c\), \(A_l=2a(b+c)\); se for \(a\times c\), \(A_l=2b(a+c)\).
Diagonais (retângulo)
Diagonal espacial: \(d=\sqrt{a^2+b^2+c^2}\).
Diagonais das faces: \(d_{ab}=\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\), \(d_{ac}=\sqrt{a^2+c^2}\), \(d_{bc}=\sqrt{b^2+c^2}\).
Planificação e perímetro útil da base
A “faixa” lateral da planificação tem área \(P_{\text{base}}\cdot c\), com \(P_{\text{base}}=2(a+b)\) se a base for \(a\times b\). Somando ainda as duas bases \(2ab\), recuperamos \(A_t\).
Conversões de volume
- \(1\ \text{dm}^3 = 1\ \text{L}\)
- \(1\ \text{m}^3 = 1000\ \text{L}\)
- \(1\ \text{L} = 1000\ \text{cm}^3\)
3) Exemplos resolvidos (contas na vertical)
-
Enunciado. Paralelepípedo retângulo com \(a=12\ \text{cm}\), \(b=7\ \text{cm}\), \(c=4\ \text{cm}\). Calcule o volume e a área total.
Ver solução
Volume
$$\begin{aligned} V&=a\cdot b\cdot c\\ &=12\cdot7\cdot4\\ &=84\cdot4\\ &=\mathbf{336\ \text{cm}^3} \end{aligned}$$Área total
$$\begin{aligned} A_t&=2(ab+ac+bc)\\ &=2(12\cdot7+12\cdot4+7\cdot4)\\ &=2(84+48+28)\\ &=2\cdot160\\ &=\mathbf{320\ \text{cm}^2} \end{aligned}$$ -
Enunciado. Caixa com base \(30\ \text{cm}\times25\ \text{cm}\) e altura \(0{,}5\ \text{m}\). Calcule o volume em litros.
Ver solução
$$\begin{aligned} 0{,}5\ \text{m}&=50\ \text{cm}\\ V&=30\cdot25\cdot50\\ &=750\cdot50\\ &=37\,500\ \text{cm}^3\\ &=\mathbf{37{,}5\ \text{L}} \end{aligned}$$ -
Enunciado. Caixa sem tampa com \(a=0{,}6\ \text{m}\), \(b=0{,}4\ \text{m}\), \(c=0{,}5\ \text{m}\). Calcule a área externa a ser pintada.
Ver solução
Área total com tampa
$$\begin{aligned} A_t&=2(ab+ac+bc)\\ &=2(0{,}6\cdot0{,}4+0{,}6\cdot0{,}5+0{,}4\cdot0{,}5)\\ &=2(0{,}24+0{,}30+0{,}20)\\ &=2\cdot0{,}74\\ &=1{,}48\ \text{m}^2 \end{aligned}$$Sem tampa (retira-se \(ab\))
$$\begin{aligned} A_{\text{pintura}}&=A_t-ab\\ &=1{,}48-0{,}24\\ &=\mathbf{1{,}24\ \text{m}^2} \end{aligned}$$ -
Enunciado. Com base \(a\times b=9\ \text{cm}\times5\ \text{cm}\) e altura \(c=12\ \text{cm}\), calcule a área lateral.
Ver solução
$$\begin{aligned} A_l&=2c(a+b)\\ &=2\cdot12\cdot(9+5)\\ &=24\cdot14\\ &=\mathbf{336\ \text{cm}^2} \end{aligned}$$ -
Enunciado. Paralelepípedo retângulo com \(a=6\ \text{cm}\), \(b=8\ \text{cm}\), \(c=24\ \text{cm}\). Calcule a diagonal espacial.
Ver solução
$$\begin{aligned} d&=\sqrt{a^2+b^2+c^2}\\ &=\sqrt{6^2+8^2+24^2}\\ &=\sqrt{36+64+576}\\ &=\sqrt{676}\\ &=\mathbf{26\ \text{cm}} \end{aligned}$$
4) Exercícios rápidos (com gabarito em abre/fecha)
-
Um bloco tem \(a=7\ \text{cm}\), \(b=4\ \text{cm}\), \(c=5\ \text{cm}\). Calcule o volume.
Gabarito
$$\begin{aligned} V&=7\cdot4\cdot5\\ &=\mathbf{140\ \text{cm}^3} \end{aligned}$$ -
Para \(a=10\ \text{cm}\), \(b=6\ \text{cm}\), \(c=12\ \text{cm}\), calcule a área total.
Gabarito
$$\begin{aligned} A_t&=2(10\cdot6+10\cdot12+6\cdot12)\\ &=2(60+120+72)\\ &=\mathbf{504\ \text{cm}^2} \end{aligned}$$ -
Uma base \(30\ \text{cm}\times20\ \text{cm}\) e altura \(50\ \text{cm}\). Calcule a área da faixa lateral (planificação).
Gabarito
$$\begin{aligned} P_{\text{base}}&=2(30+20)=100\ \text{cm}\\ A_{\text{faixa}}&=P_{\text{base}}\cdot c=100\cdot50=\mathbf{5000\ \text{cm}^2} \end{aligned}$$
5) Perguntas frequentes
| Quando usar \(V=a\cdot b\cdot c\) e quando \(V=A_{\text{base}}\cdot h\)? | No retângulo (arestas perpendiculares) use \(a\cdot b\cdot c\). Em paralelepípedo oblíquo, use \(A_{\text{base}}\cdot h\) com altura perpendicular. |
|---|---|
| Qual a diferença entre área total e lateral? | Área total soma as 6 faces; a lateral soma apenas as 4 faces laterais (sem as duas bases). |
| Como converter para litros? | \(1\ \text{L}=1000\ \text{cm}^3\) e \(1\ \text{m}^3=1000\ \text{L}\). |